The query below lists all table (and view) constraints - primary keys, unique key constraints and indexes, foreign keys and check and default constraints.
Query
select table_view,
object_type,
constraint_type,
constraint_name,
details
from (
select schema_name(t.schema_id) + '.' + t.[name] as table_view,
case when t.[type] = 'U' then 'Table'
when t.[type] = 'V' then 'View'
end as [object_type],
case when c.[type] = 'PK' then 'Primary key'
when c.[type] = 'UQ' then 'Unique constraint'
when i.[type] = 1 then 'Unique clustered index'
when i.type = 2 then 'Unique index'
end as constraint_type,
isnull(c.[name], i.[name]) as constraint_name,
substring(column_names, 1, len(column_names)-1) as [details]
from sys.objects as t
left outer join sys.indexes as i
on t.object_id = i.object_id
left outer join sys.key_constraints as c
on i.object_id = c.parent_object_id
and i.index_id = c.unique_index_id
cross apply (select col.[name] + ', '
from sys.index_columns as ic
inner join sys.columns as col
on ic.object_id = col.object_id
and ic.column_id = col.column_id
where ic.object_id = t.object_id
and ic.index_id = i.index_id
order by col.column_id
for xml path ('') ) as D (column_names)
where is_unique = 1
and t.is_ms_shipped <> 1
union all
select schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name as foreign_table,
'Table',
'Foreign key',
fk.name as fk_constraint_name,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name
from sys.foreign_keys as fk
inner join sys.tables as fk_tab
on fk_tab.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
inner join sys.tables as pk_tab
on pk_tab.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
inner join sys.foreign_key_columns as fk_cols
on fk_cols.constraint_object_id = fk.object_id
union all
select schema_name(t.schema_id) + '.' + t.[name],
'Table',
'Check constraint',
con.[name] as constraint_name,
con.[definition]
from sys.check_constraints as con
left outer join sys.objects as t
on con.parent_object_id = t.object_id
left outer join sys.all_columns as col
on con.parent_column_id = col.column_id
and con.parent_object_id = col.object_id
union all
select schema_name(t.schema_id) + '.' + t.[name],
'Table',
'Default constraint',
con.[name],
col.[name] + ' = ' + con.[definition]
from sys.default_constraints as con
left outer join sys.objects as t
on con.parent_object_id = t.object_id
left outer join sys.all_columns as col
on con.parent_column_id = col.column_id
and con.parent_object_id = col.object_id) as a
order by table_view, constraint_type, constraint_name
Columns
- table_view - table or view schema and name
- object_type - object type:
- Table
- View
- constraint_type - type of constraint:
- Primary key
- Unique key
- Foreign key
- Check constraint
- Default constraint
- constraint_name - name of constraint or index
- details - details of this constraint:
- Primary key - PK column(s)
- Unique key - UK column(s)
- Foreign key - parent table name
- Check constraint - check definition
- Default constraint - column name and default value definition
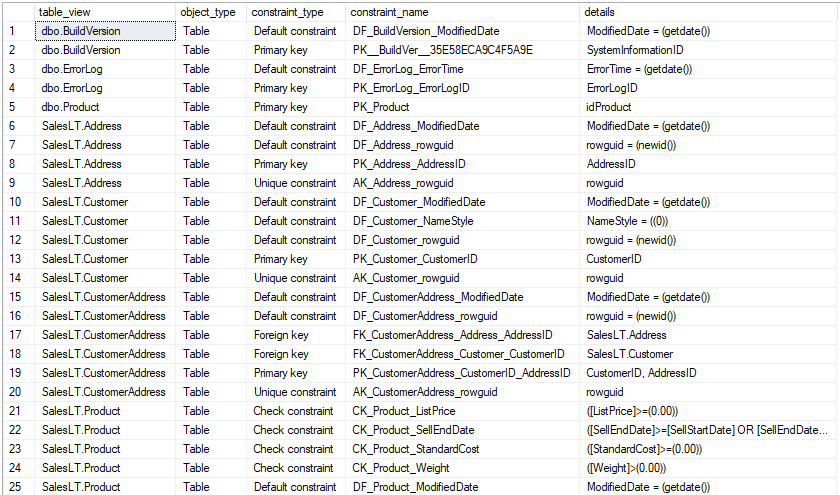
Rows
- One row: represents one constraint: PK, UK, FK, Check, Default
- Scope of rows: all constraints
- Ordered by: schema, table name, constraint type
Sample results











 Rene Castro
Rene Castro