Query below returns all primary keys and unique constraints on tables in IBM DB2 database.
Check out also list of unique keys.
Query
select tab.tabschema || '.' || tab.tabname as table_name,
tab.constname as constraint_name,
case when tab.type = 'P' then 'PRIMARY KEY'
else 'UNIQUE'
end as constraint_type,
listagg(key.colname, ', ')
within group(order by key.colseq) as columns,
ind.indname as index_name,
case ind.indextype
when 'BLOK' then 'Block index'
when 'REG' then 'Regular index'
when 'CPMA' then 'Page map index for a column-organized table'
when 'RCT ' then 'Key sequence index for a range-clustered table'
when 'CLUS' then 'Clustering index'
when 'TEXT' then 'Text index'
when 'DIM' then 'Dimension block index'
when 'XPTH' then 'XML path index'
when 'XRGN' then 'XML region index'
when 'XVIL' then 'Index over XML column (logical)'
when 'XVIP' then 'Index over XML column (physical)'
end as index_type
from syscat.tabconst tab
join syscat.keycoluse key
on tab.tabschema = key.tabschema
and tab.tabname = key.tabname
and tab.constname = key.constname
join syscat.constdep dep
on tab.constname = dep.constname
and tab.tabschema = dep.tabschema
and tab.tabname = dep.tabname
join syscat.indexes ind
on dep.bschema = ind.indschema
and dep.bname = ind.indname
where tab.tabschema not like ('SYS%')
and tab.type in ('P','U')
group by tab.tabschema,
tab.constname,
tab.tabname,
tab.type,
ind.indname,
ind.indextype
order by table_name;
Columns
- table_name - name of the table with schema name
- constraint_name - constraint name of primary key or unique constraint
- constraint_type - type of the constraint
- PRIMARY KEY
- UNIQUE
- columns - columns separated with ","
- index_name - name of index used by constraint
- index_type - type of index:
- Block index
- Regular index
- Page map index for a column-organized table
- Key sequence index for a range-clustered table
- Clustering index
- Text index
- Dimension block index
- XML path index
- XML region index
- Index over XML column (logical)
- Index over XML column (physical)
Rows
- One row represents one constraint in the database.
- Scope of rows: all PKs, and unique constraints
- Ordered by schema and table name
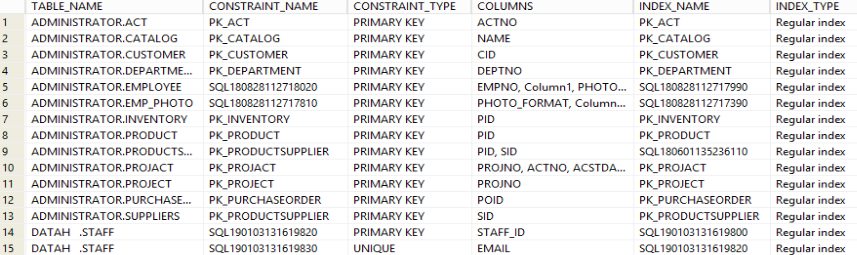
Sample results











 Bart Gawrych
Bart Gawrych