This query works on SQL Server 2016 or newer.
SQL Server 2016 brought exciting and useful feature - system-versioned temporal tables that implement change tracking managed by server itself. Server manages 2 separate tables - system-versioned temporal table with actual data and history table that stores change history.
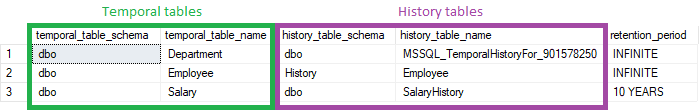
Query below returns temporal tables paired with their history tables and retention period (how long history is stored).
Query
select schema_name(t.schema_id) as temporal_table_schema,
t.name as temporal_table_name,
schema_name(h.schema_id) as history_table_schema,
h.name as history_table_name,
case when t.history_retention_period = -1
then 'INFINITE'
else cast(t.history_retention_period as varchar) + ' ' +
t.history_retention_period_unit_desc + 'S'
end as retention_period
from sys.tables t
left outer join sys.tables h
on t.history_table_id = h.object_id
where t.temporal_type = 2
order by temporal_table_schema, temporal_table_name
Columns
- temporal_table_schema - temporal table schema name
- temporal_table_name - temporal table name
- history_table_schema - history table schema name
- history_table_name - history table name
- retention_period - retention period - how long history is preserved (defined by DBA). Example values: INFINITE, 6 MONTHS, 30 DAYS
Rows
- One row represents one temporal table
- Scope of rows: only temporal tables defined in a database
- Ordered by temporal table schema and table name
Sample results
Query returns 3 tables:
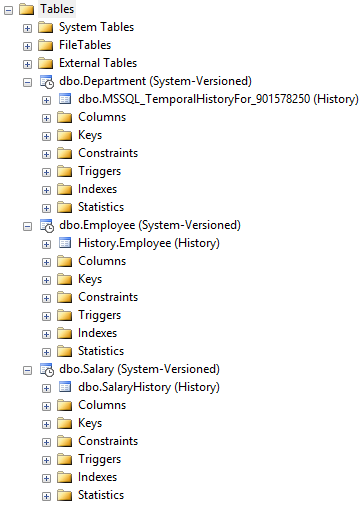
And this is how it looks in SSMS:











 Piotr Kononow
Piotr Kononow