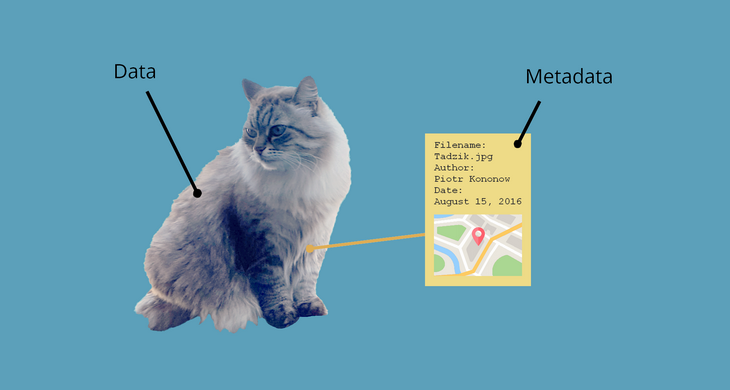
Metadata is simply data about data. It means it is a description and context of the data. It helps to organize, find and understand data. Here are a few real world examples of metadata:
Typical metadata
Those are some typical metadata elements:
- Title and description,
- Tags and categories,
- Who created and when,
- Who last modified and when,
- Who can access or update.
A photo

Every time you take a photo with today's cameras a bunch of metadata is gathered and saved with it:
- date and time,
- filename,
- camera settings,
- geolocation.
A book

Each book has a number of standard metadata on the covers and inside. This includes:
- a title,
- author name,
- publisher and copyright details,
- description on a back,
- table of contents,
- index,
- page numbers.
A blog post
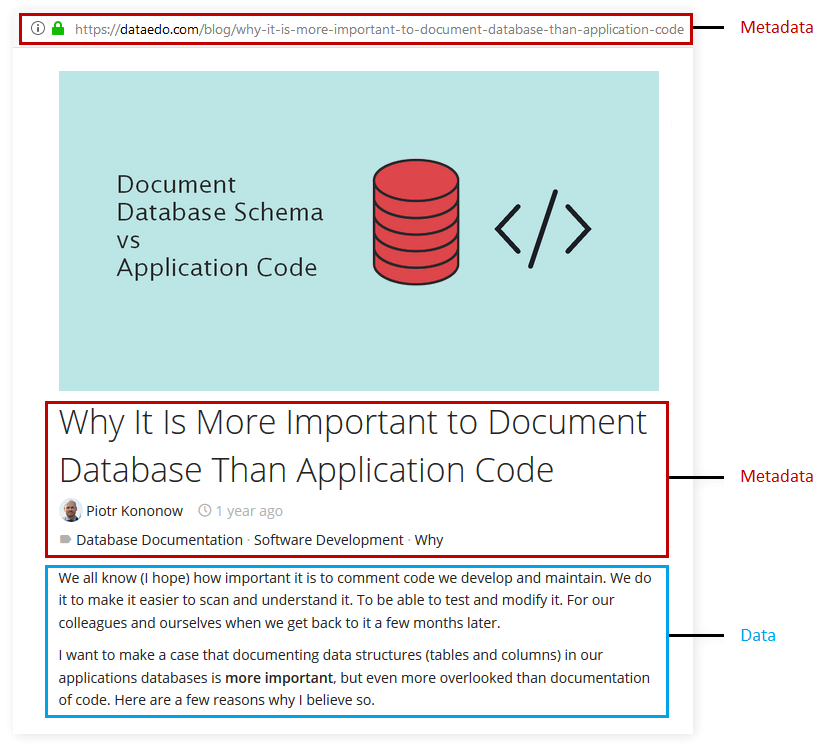
Every blog post has standard metadata fields that are usually at before first paragraph. This includes:
- title,
- author,
- published time,
- category,
- tags.
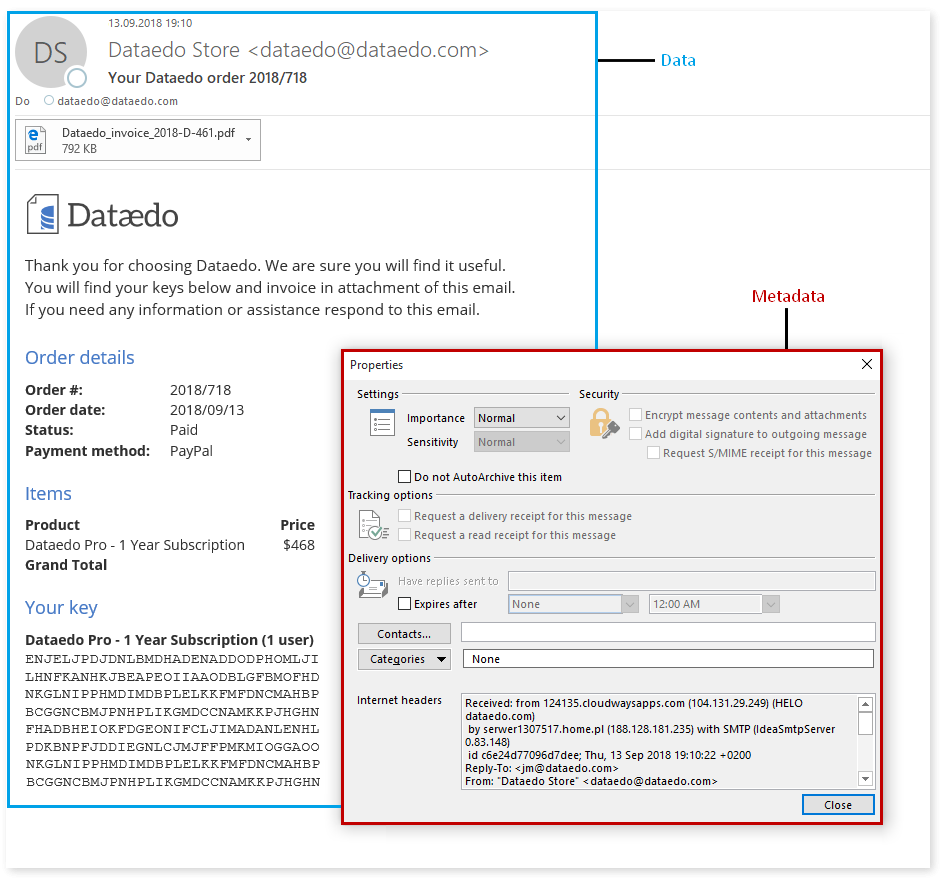
Every email you send or receive has a number of metadata fields, many of which are hidden in the message header and not visible to you in your mail client. This metadata includes:
- subject,
- from,
- to,
- date and time sent,
- sending and receiving server names and IPs,
- format (plain text of HTLM),
- anti-spam software details.
Word document
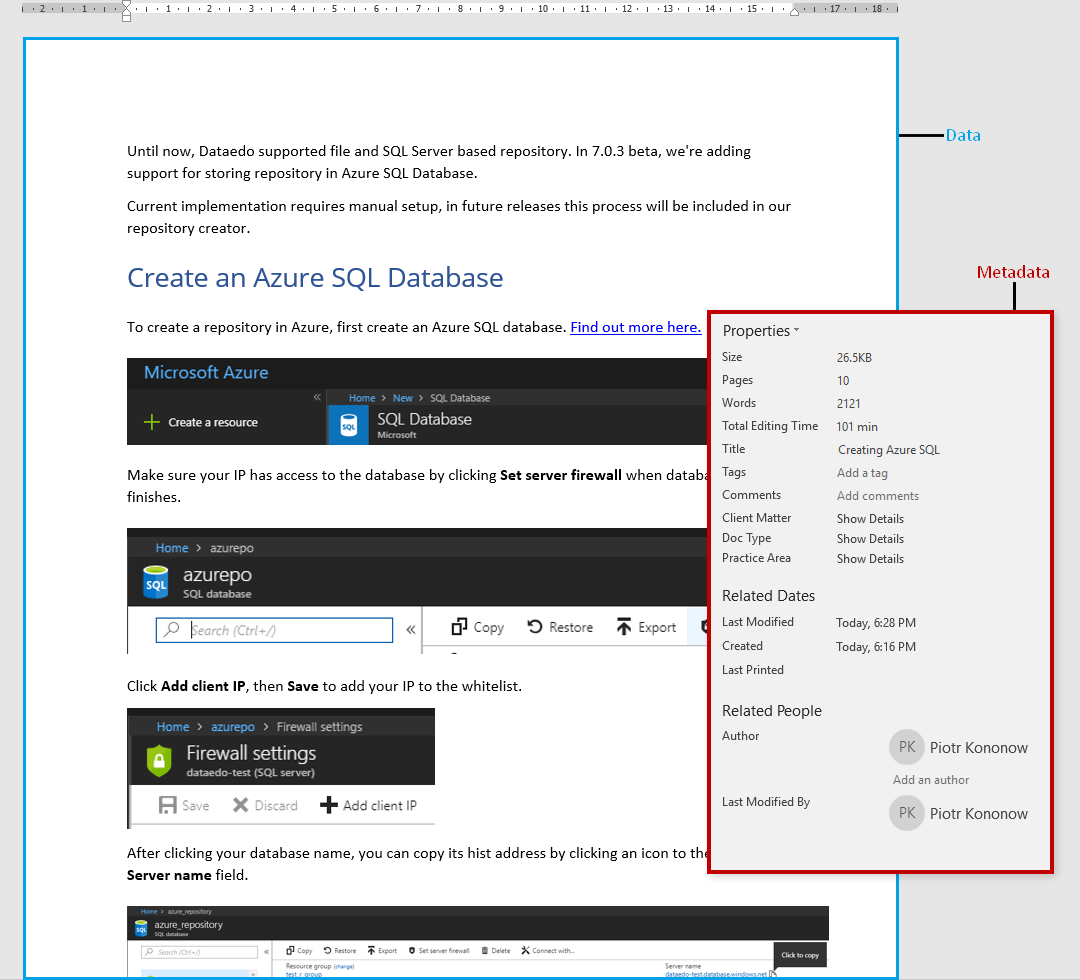
Every word processing software collects some standard metadata and enables you to add your own fields for each document. Typical fields are:
- title,
- subject,
- author,
- company,
- status,
- creation date and time,
- last modification date and time,
- number of pages.
A spreadsheet
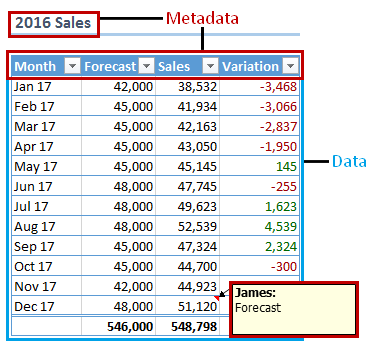
Spreadsheets contain a few metadata fields:
- tab names,
- table names,
- column names,
- user comments.
Relational database
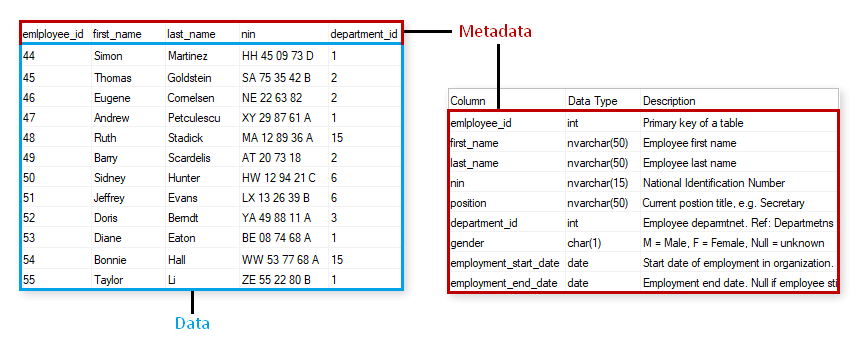
Relational databases (most common type of database) store and provide access not only data but also metadata in a structure called data dictionary or system catalog. It holds information about:
- tables,
- columns,
- data types,
- constraints
- table relationships,
- and many more
Browse sample database metadata
Learn more about metadata in relational databases
Computer files
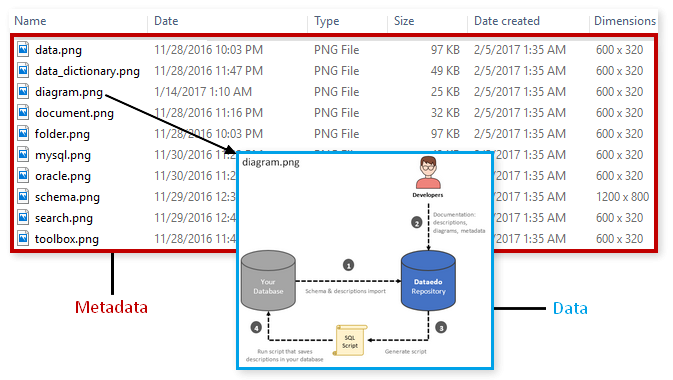
All the fields you see by each file in file explorer is actually metadata. The actual data is inside those files. Metadata includes:
- file name,
- type,
- size,
- creation date and time,
- last modification date and time.
Web page
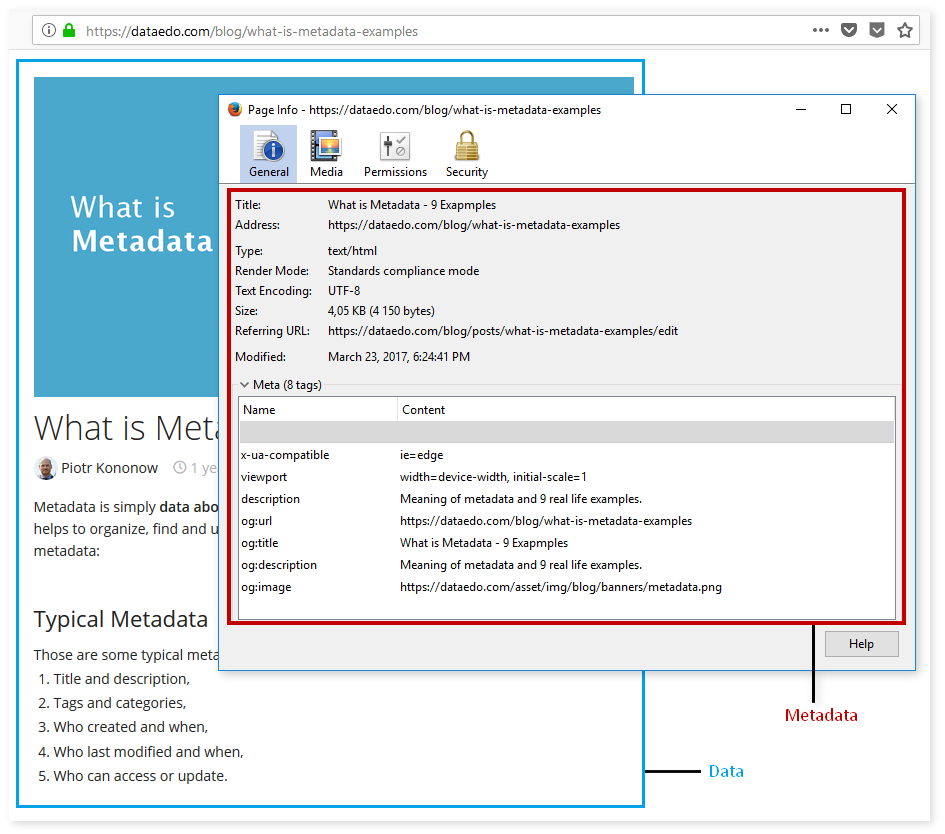
Every web page has a number of metadata fields:
- page title,
- page description,
- icon.
Paper files

Paper document files have often administrative metadata that help manage documents. This might include:
- letter for files organized alphabetically,
- access control information ("classified" for instance),
- logos.
Summary
Those were my examples. I hope by now you have pretty good understanding of what metadata is. If you are looking for a solution that will help you manage your metadata, check out Dataedo - metadata management software.











 Piotr Kononow
Piotr Kononow