Let me start with reminding what metadata is. Metadata is data about data (see those examples to better understand this concept).
Data in relational databases is stored in structured manner, organized in tables and columns and extended with constraints on the data - primary and unique constraints, foreign keys, check constraints or data types. All those rules defined in a database are called database schema.
In case of relational databases metadata refers to information on their schema and all the other information regarding access, storage, built in programs or any other information about database elements or usage.
Typical metadata in databases
Schema
- Tables
- Columns
- Constraints
- Foreign keys
- Indexes
- Sequences
Programs
- Views
- User defined functions
- Stored procedures
- Triggers
Security
- Users
- User groups
- Privileges
Physical implementation
- Partitions
- Files
- Backups
Storage
- Size of tables and indexes in KBs
- Number of rows in tables
Auditing
- Sessions
- Connection history
- Query history
Accessing metadata
Most popular databases provide access to their metadata with a set of tables or views often called system catalog or data dictionary. Many of them implement or standard information schema. You can access those views using plain SQL.
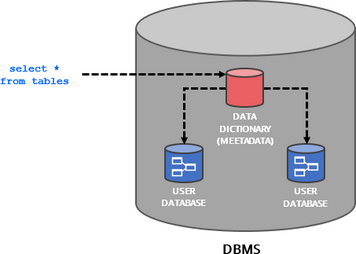
Managing metadata
If you are looking for a solution that will help you manage your metadata, check out Dataedo - metadata management software.











 Piotr Kononow
Piotr Kononow