The query below returns foreign key constraint columns defined in a database.
Query
select schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name as foreign_table,
'>-' as rel,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name as primary_table,
fk_cols.constraint_column_id as no,
fk_col.name as fk_column_name,
' = ' as [join],
pk_col.name as pk_column_name,
fk.name as fk_constraint_name
from sys.foreign_keys as fk
inner join sys.tables as fk_tab
on fk_tab.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
inner join sys.tables as pk_tab
on pk_tab.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
inner join sys.foreign_key_columns as fk_cols
on fk_cols.constraint_object_id = fk.object_id
inner join sys.columns as fk_col
on fk_col.column_id = fk_cols.parent_column_id
and fk_col.object_id = fk_tab.object_id
inner join sys.columns as pk_col
on pk_col.column_id = fk_cols.referenced_column_id
and pk_col.object_id = pk_tab.object_id
order by schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name,
fk_cols.constraint_column_id
Columns
- foreign_table - foreign table name with schema name
- rel - relationship symbol implicating direction
- primary_table - primary (referenced) table name with schema name
- no - id of the column in key. Single column keys always have 1, composite keys have 1, 2, ... n for each column of the key
- fk_column_name - foreign table column
- join - "=" symbol indicating join operation for pair of columns
- pk_column_name - primary (referenced) table column
- fk_constraint_name - foreign key constraint name
Rows
- One row: represents one foreign key column. If the foreign key consists of multiple columns (composite key), each column appears separately.
- Scope of rows: all foreign keys in a database and their columns
- Ordered by: foreign table schema name and table name and column ordinal position in the key
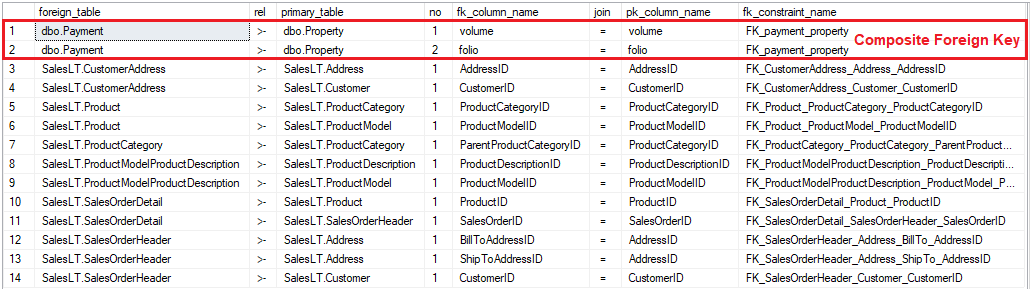
Sample results
Foreign key constraints in the AdventureWorksLT database with their columns:











 Rene Castro
Rene Castro