This is a collection of queries for SQL Server system catalog (data dictionary) that help you find information about foreign keys. If you are interested in schema and metadata analysis have a look at:
Basic queries
1. Foreign keys: row per column
One row represents one foreign key column. If foreign key consists of multiple columns (composite key), each column appears separately.
select schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name as foreign_table,
'>-' as rel,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name as primary_table,
fk_cols.constraint_column_id as no,
fk_col.name as fk_column_name,
' = ' as [join],
pk_col.name as pk_column_name,
fk.name as fk_constraint_name
from sys.foreign_keys fk
inner join sys.tables fk_tab
on fk_tab.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
inner join sys.tables pk_tab
on pk_tab.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
inner join sys.foreign_key_columns fk_cols
on fk_cols.constraint_object_id = fk.object_id
inner join sys.columns fk_col
on fk_col.column_id = fk_cols.parent_column_id
and fk_col.object_id = fk_tab.object_id
inner join sys.columns pk_col
on pk_col.column_id = fk_cols.referenced_column_id
and pk_col.object_id = pk_tab.object_id
order by schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name,
fk_cols.constraint_column_id
Sample results:
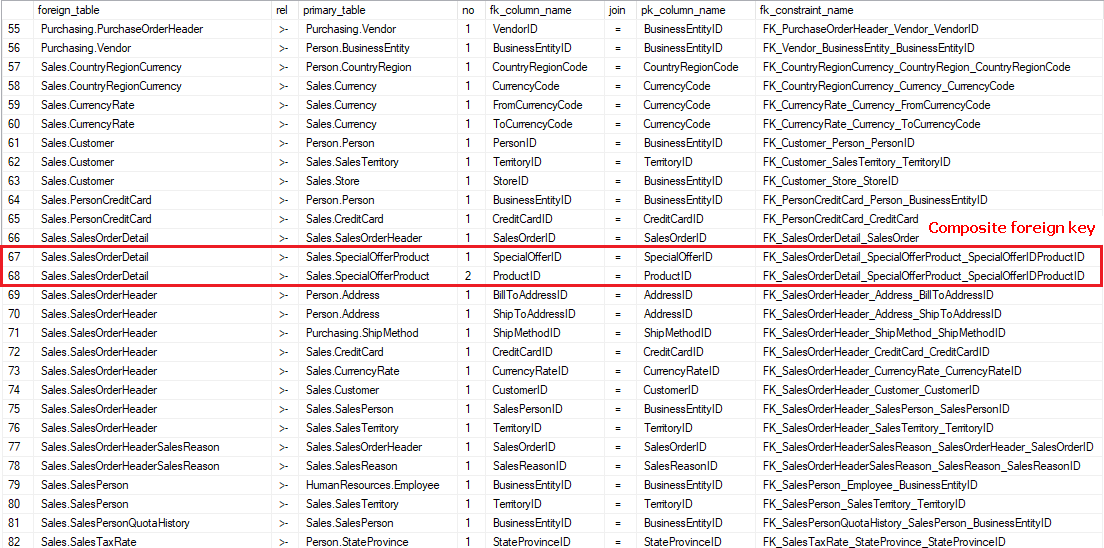
Columns:
- foreign_table - foreign table name with schema name
- rel - relationship symbol implicating direction
- primary_table - primary (referenced) table name with schema name
- no - id of the column in key. Single column keys always have 1, composite keys have 1, 2, ... n for each column of the key
- fk_column_name - foreign table column
- join - "=" symbol indicating join operation for pair of columns
- pk_column_name - primary (referenced) table column
- fk_constraint_name - foreign key constraint name
2. Foreign keys: row per key
One row represents one foreign key. If foreign key consists of multiple columns (composite key) it is still represented as one row.
select schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name as foreign_table,
'>-' as rel,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name as primary_table,
substring(column_names, 1, len(column_names)-1) as [fk_columns],
fk.name as fk_constraint_name
from sys.foreign_keys fk
inner join sys.tables fk_tab
on fk_tab.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
inner join sys.tables pk_tab
on pk_tab.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
cross apply (select col.[name] + ', '
from sys.foreign_key_columns fk_c
inner join sys.columns col
on fk_c.parent_object_id = col.object_id
and fk_c.parent_column_id = col.column_id
where fk_c.parent_object_id = fk_tab.object_id
and fk_c.constraint_object_id = fk.object_id
order by col.column_id
for xml path ('') ) D (column_names)
order by schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name
Sample results:
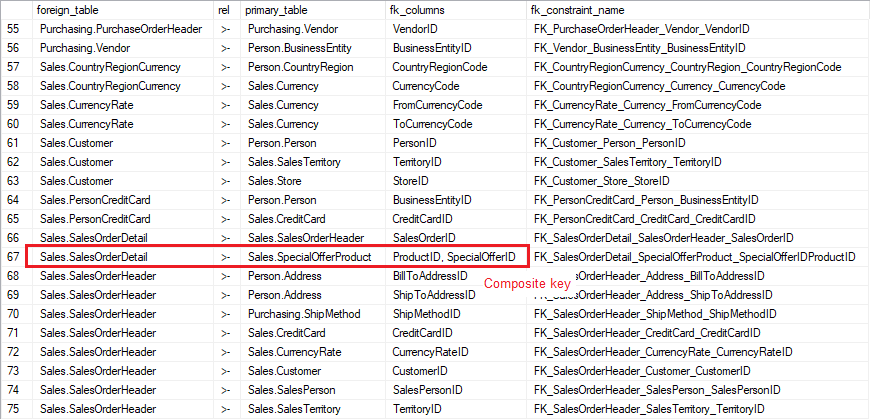
Columns:
- foreign_table - foreign table name with schema name
- rel - relationship symbol implicating direction
- primary_table - primary (referenced) table name with schema name
- fk_columns - list of FK column names, separated with ","
- fk_constraint_name - foreign key constraint name
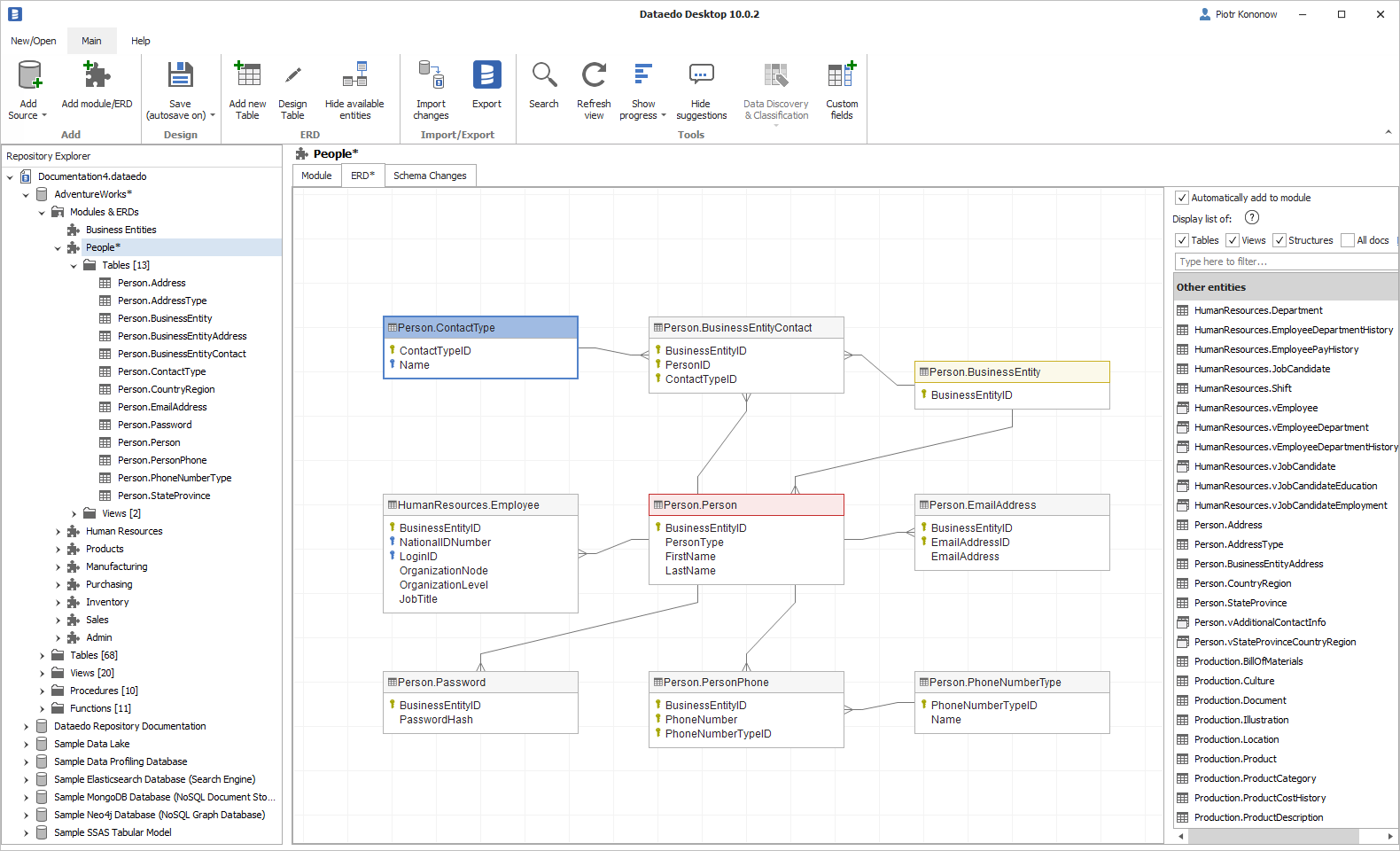
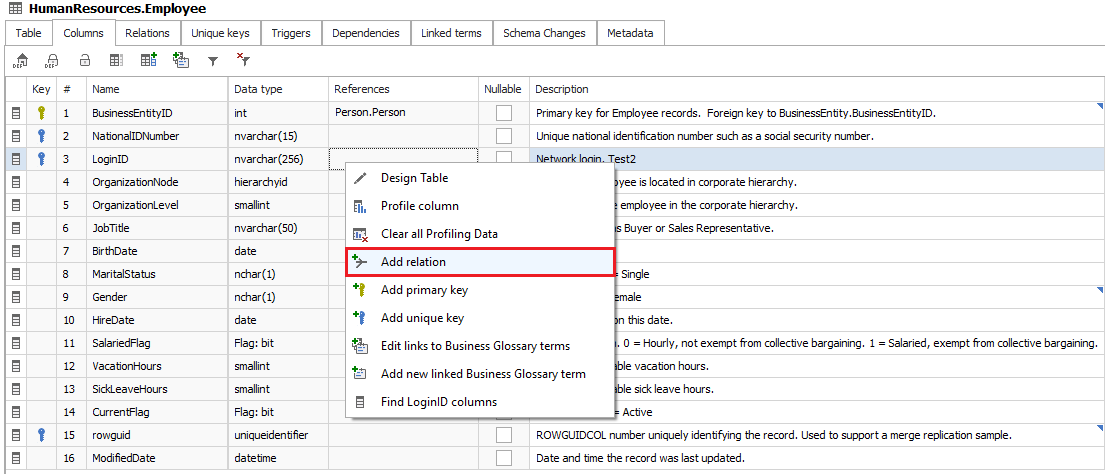
Visualize foreign keys
Listing foreign keys is very useful, but it's also really beneficial to visualize foreign keys with ER diagrams (ERDs). Dataedo allows you to import schema from your database, describe each field and visualize quickly with several small, manageable diagrams.
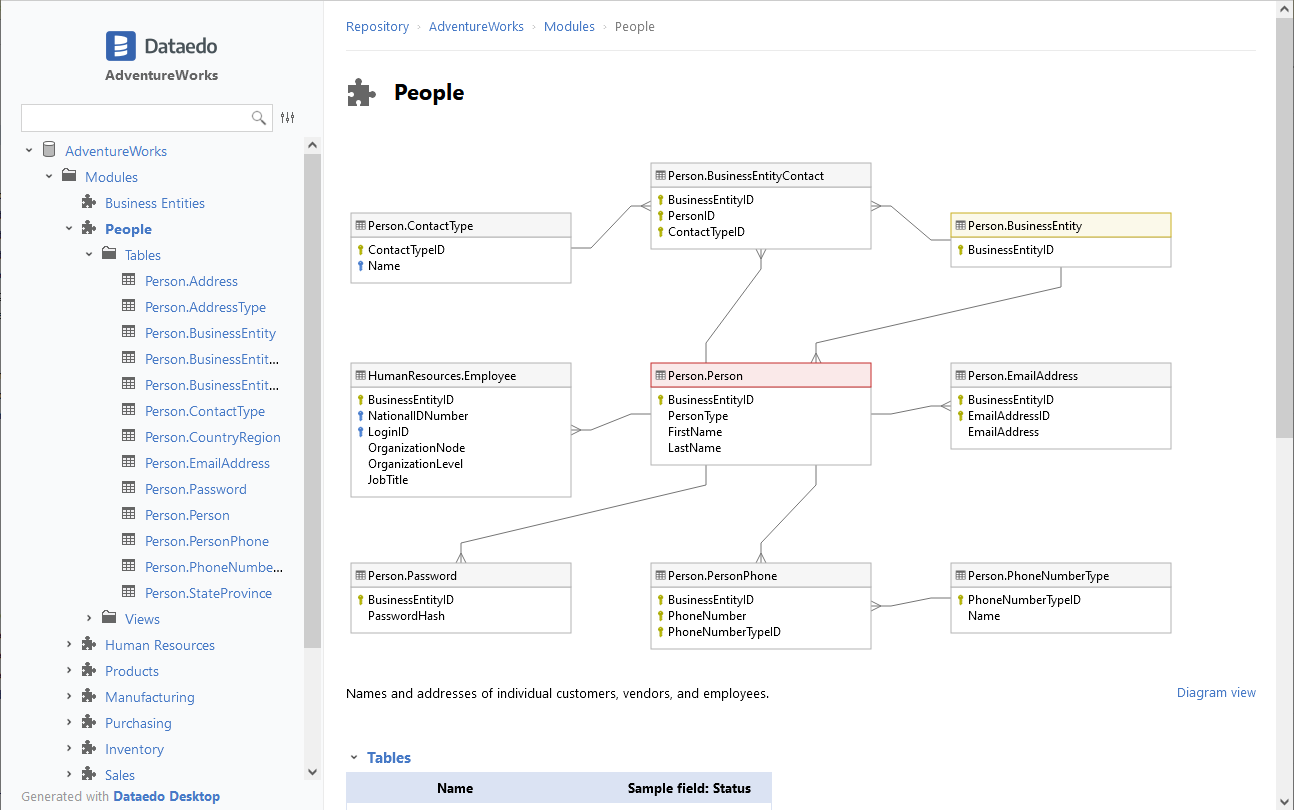
Then, finally, you can share complete documentation, with diagrams and data dictionary in HTML, PDF or on prem web portal.
More queries
3. All columns and their FKs (if present)
Query below returns all columns from all tables in a database with a foreign key reference if column has one.
select schema_name(tab.schema_id) + '.' + tab.name as [table],
col.column_id,
col.name as column_name,
case when fk.object_id is not null then '>-' else null end as rel,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name as primary_table,
pk_col.name as pk_column_name,
fk_cols.constraint_column_id as no,
fk.name as fk_constraint_name
from sys.tables tab
inner join sys.columns col
on col.object_id = tab.object_id
left outer join sys.foreign_key_columns fk_cols
on fk_cols.parent_object_id = tab.object_id
and fk_cols.parent_column_id = col.column_id
left outer join sys.foreign_keys fk
on fk.object_id = fk_cols.constraint_object_id
left outer join sys.tables pk_tab
on pk_tab.object_id = fk_cols.referenced_object_id
left outer join sys.columns pk_col
on pk_col.column_id = fk_cols.referenced_column_id
and pk_col.object_id = fk_cols.referenced_object_id
order by schema_name(tab.schema_id) + '.' + tab.name,
col.column_id
Sample results:
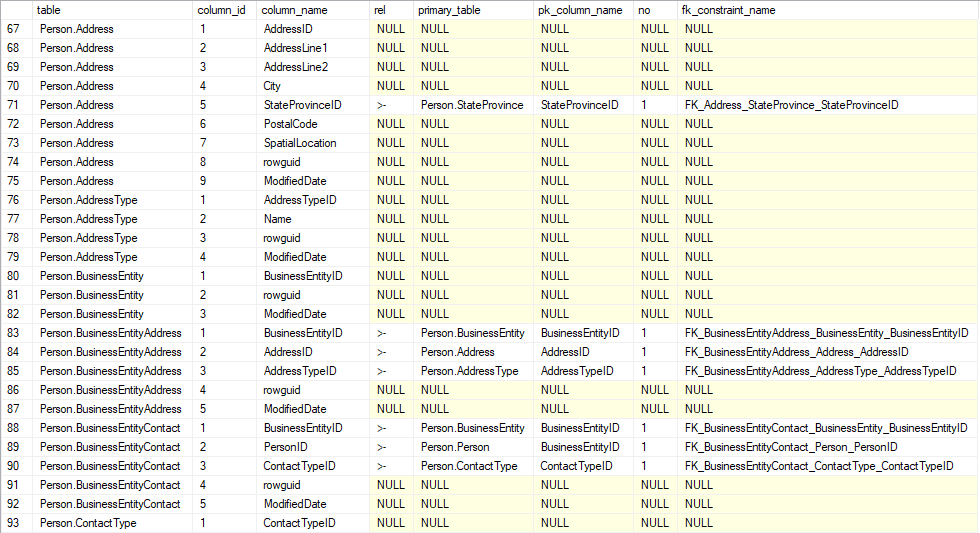
Columns:
- table - table in a database with schema name
- column_id - number of column in a database
- column_name - column name
- rel - relationship symbol ('>-') indicating foreign key and direction
- primary_table - referenced table
- pk_column_name - referenced column
- no - column id in a key constraint
- fk_constraint_name - foreign key constraint name
4. All tables referenced by specific table
Query below lists all tables referenced with foreign key by specific table.
Please note: There can be more tables with the same name. If that's the case, uncomment where clause and provide schema name.
select distinct
schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name as foreign_table,
'>-' as rel,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name as primary_table
from sys.foreign_keys fk
inner join sys.tables fk_tab
on fk_tab.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
inner join sys.tables pk_tab
on pk_tab.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
where fk_tab.[name] = 'Your table' -- enter table name here
-- and schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) = 'Your table schema name'
order by schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name
Sample results:
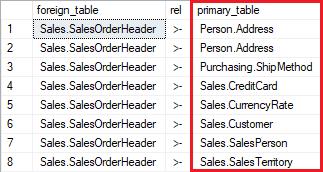
Columns:
- foreign_table - foreign table name with schema name - the table you provided as a parameter
- foreign_table - relationship symbol implicating FK and direction
- primary_table - primary (referenced) tables names with schema name - the tables you are looking for
5. All tables referencing specific table
Query below lists all tables that reference specific table with foreign keys.
Please note: There can be more tables with the same name. If that's the case, uncomment where clause and provide schema name.
select distinct
schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name as foreign_table,
'>-' as rel,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name as primary_table
from sys.foreign_keys fk
inner join sys.tables fk_tab
on fk_tab.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
inner join sys.tables pk_tab
on pk_tab.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
where pk_tab.[name] = 'Your table' -- enter table name here
-- and schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) = 'Your table schema name'
order by schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name,
schema_name(pk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + pk_tab.name
Sample results:
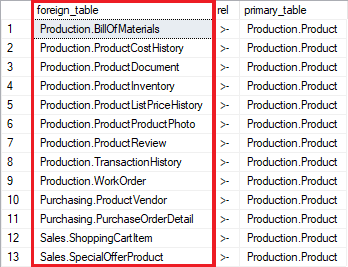
Columns:
- foreign_table - foreign tables schemas and names - the table you are looking for
- foreign_table - relationship symbol implicating FK and direction
- primary_table - primary (referenced) tables names with schema name - the table you provided as a parameter
What if foreign key constraints are note defined in your database?
Many databases, even major applications from Microsoft, Oracle or SAP do not have foreign key constraints in their schema. That means you can't discover relationships with queries in this article. There are many reasons for why that is.
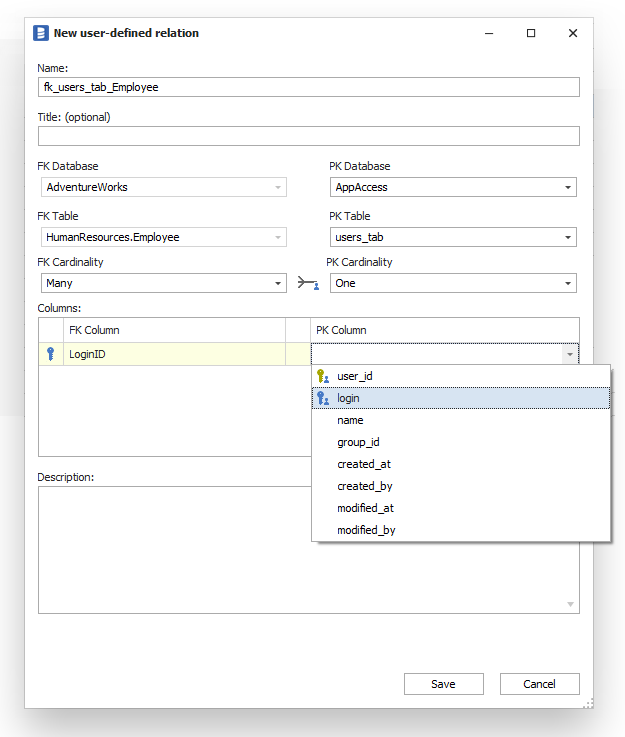
What if your database looked more like this?
Well, in that case you can always document foreign keys in your database with Dataedo. Simply connect to your database, import schema to local repository and define relationships (but also, keys, descriptions, aliases, and more). That will give you (and everyone using or designing the database) reference documentation, and you will be able to create ER diagrams, too.
Statistical queries
6. Most referenced tables
Query below lists tables that are most referenced by other tables with foreign keys. Those are the dictionary tables such as person, product or store. In data warehouses those are dimension tables.
select schema_name(tab.schema_id) + '.' + tab.name as [table],
count(fk.name) as [references],
count(distinct fk.parent_object_id) as referencing_tables
from sys.tables as tab
left join sys.foreign_keys as fk
on tab.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
group by schema_name(tab.schema_id), tab.name
having count(fk.name) > 0
order by 2 desc
Sample results:
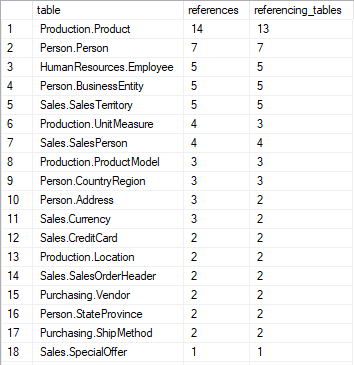
Columns:
- table - name of the table with schema name
- references - number of foreign keys referencing to this table
- referencing_tables - number of different tables referencing to this table
7. Tables with most FKs
Query below lists tables with their number of foreign keys and number of tables they refer to.
select schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name as [table],
count(*) foreign_keys,
count (distinct referenced_object_id) referenced_tables
from sys.foreign_keys fk
inner join sys.tables fk_tab
on fk_tab.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
group by schema_name(fk_tab.schema_id) + '.' + fk_tab.name
order by count(*) desc
Sample results:
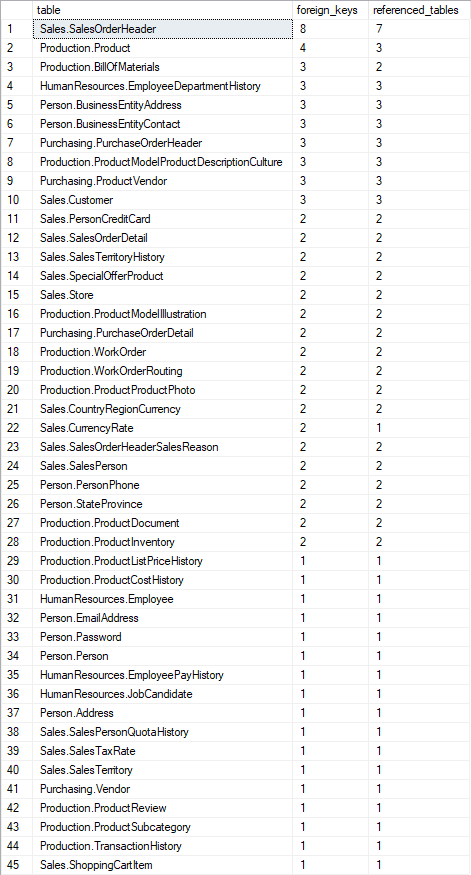
Columns:
- table - table with schema name
- foreign_keys - number of foreign keys in a table
- referenced_tables - number of referenced tables. Note that it is not the same as number of foreign keys, as multiple foreign keys may reference the same table.
Create documentation of your databases in minutes
You can get interactive HTML documetation of your database in a couple of minutes with Dataedo.











 Piotr Kononow
Piotr Kononow